TRIANGLE
TRIANGLE
- Geometry, a triangle is a three-sided polygon that consists of three edges and three vertices.
- The most important property of a triangle is that the sum of the internal angles of a triangle is equal to 180 degrees
- As we discussed in the introduction, a triangle is a type of polygon, which has three sides, and the two sides are joined end to end is called the vertex of the triangle.
- An angle is formed between two sides. This is one of the important parts of geometry.
On the basis of length of the sides, triangles are classified into three categories:
1. Scalene Triangle
2. Isosceles Triangle
3. Equilateral Triangle
On the basis of measurement of the angles, triangles are classified into three categories:
1. Acute Angle Triangle
2. Right Angle Triangle
3. Obtuse Angle Triangle
Scalene Triangle
- A scalene triangle is a type of triangle, in which all the three sides have different side measures.
- Due to this, the three angles are also different from each other.
- In an isosceles triangle, two sides have equal length.
- The two angles opposite to the two equal sides are also equal to each other.
- An equilateral triangle has all three sides equal to each other.
- Due to this all the internal angles are of equal degrees, i.e. each of the angles is 60°.
- An acute triangle has all of its angles less than 90°.
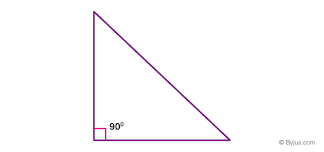
- In a right triangle, one of the angles is equal to 90° or right angle.
- An obtuse triangle has any of its one angles more than 90°.
- A perimeter of a triangle is defined as the total length of the outer boundary of the triangle.
- we can say, the perimeter of the triangle is equal to the sum of all its three sides.
- The unit of the perimeter is same as the unit of sides of the triangle.
If ABC is a triangle, where AB, BC and AC are the lengths of its sides, then the perimeter of ABC is given by:
- The area of triangle is the region occupied by the triangle in 2d space.
- The area for different triangles varies from each other depending on their dimensions.
- We can calculate the area if we know the base length and the height of a triangle.
- It is measured in square units.
Suppose a triangle with base ‘B’ and height ‘H’ is given to us, then, the area of a triangle is given by-
Area of triangle = Half of Product of Base and Height Area = 1/2 × Base × Height |
- Sum of angles of the triangle is equal to 180 degrees.
- Exterior angles of a triangle add up to 360 degrees.
- Shortest side is always opposite the smallest angle of a triangle.
1.Find the area of a triangle having base equal to 9 cm and height equal to 6 cm.
= 1/2 × 9 × 6 cm2
= 27 cm2
BC = 26 units
AB = 10 units
BC is the longest side of the triangle
According to Pythagoras rule:
BC2 = AB2 + AC2
262 = 102 + AC2
AC2 = 676 – 100 = 576
Therefore, AC = 24 units
We know that the area of a right-angled triangle = ½ * product of the two perpendicular sides = ½ * AB * AC = ½ * 10 * 24 = 120 sq. units
.jpg)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)